Four common misconceptions about quantum physics
Quantum mechanics, the theory which rules the microworld of atoms and particles, certainly has the X factor. Unlike many other areas of physics, it is bizarre and counter-intuitive, which makes it dazzling and intriguing. When the 2022 Nobel prize in physics was awarded to Alain Aspect, John Clauser and Anton Zeilinger for research shedding light on quantum mechanics, it sparked excitement and discussion.
But debates about quantum mechanics – be they on chat forums, in the media or in science fiction – can often get muddled thanks to a number of persistent myths and misconceptions. Here are four.
1. A cat can be dead and alive
Erwin Schrödinger could probably never have predicted that his thought experiment, Schrödinger’s cat, would attain internet meme status in the 21st century.
It suggests that an unlucky feline stuck in a box with a kill switch triggered by a random quantum event – radioactive decay, for example – could be alive and dead at the same time, as long as we don’t open the box to check.
We’ve long known that quantum particles can be in two states – for example in two locations – at the same time. We call this a superposition.
Scientists have been able to show this in the famous double-slit experiment, where a single quantum particle, such as a photon or electron, can go through two different slits in a wall simultaneously. How do we know that?
In quantum physics, each particle’s state is also a wave. But when we send a stream of photons – one by one – through the slits, it creates a pattern of two waves interfering with each other on a screen behind the slit. As each photon didn’t have any other photons to interfere with when it went through the slits, it means it must simultaneously have gone through both slits – interfering with itself (image below).
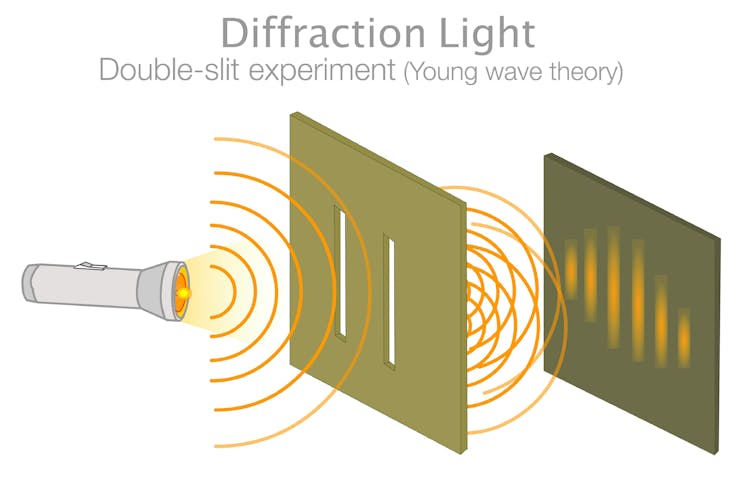
For this to work, however, the states (waves) in the superposition of the particle going through both slits need to be “coherent” – having a well defined relationship with each other.
These superposition experiments can be done with objects of ever increasing size and complexity. One famous experiment by Anton Zeilinger in 1999 demonstrated quantum superposition with large molecules of Carbon-60 known as “buckyballs”.
So what does this mean for our poor cat? Is it really both alive and dead as long as we don’t open the box? Obviously, a cat is nothing like an individual photon in a controlled lab environment, it is much bigger and more complex. Any coherence that the trillions upon trillions of atoms that make up the cat might have with each other is extremely shortlived.
This does not mean that quantum coherence is impossible in biological systems, just that it generally won’t apply to big creatures such as cats or a human.
2. Simple analogies can explain entanglement
Entanglement is a quantum property which links two different particles so that if you measure one, you automatically and instantly know the state of the other – no matter how far apart they are.
Common explanations for it typically involve everyday objects from our classical macroscopic world, such as dice, cards or even pairs of odd-coloured socks. For example, imagine you tell your friend you have placed a blue card in one envelope and an orange card in another. If your friend takes away and opens one of the envelopes and finds the blue card, they will know you have the orange card.
But to understand quantum mechanics, you have to imagine the two cards inside the envelopes are in a joint superposition, meaning they are both orange and blue at the same time (specifically orange/blue and blue/orange). Opening one envelope reveals one colour determined at random. But opening the second still always reveals the opposite colour because it is “spookily” linked to the first card.
One could force the cards to appear in a different set of colours, akin to doing another type of measurement. We could open an envelope asking the question: “Are you a green or a red card?”. The answer would again be random: green or red. But crucially, if the cards were entangled, the other card would still always yield the opposite outcome when asked the same question.
Albert Einstein attempted to explain this with classical intuition, suggesting the cards could have been provided with a hidden, internal instruction set which told them in what colour to appear given a certain question. He also rejected the apparent “spooky” action between the cards that seemingly allows them to instantly influence each other, which would mean communication faster than the speed of light, something forbidden by Einstein’s theories.
However, Einstein’s explanation was subsequently ruled out by Bell’s theorem (a theoretical test created by the physicist John Stewart Bell) and experiments by 2022’s Nobel laureates. The idea that measuring one entangled card changes the state of the other is not true. Quantum particles are just mysteriously correlated in ways we can’t describe with everyday logic or language – they don’t communicate while also containing a hidden code, as Einstein had thought. So forget about everyday objects when you think about entanglement.
3. Nature is unreal and ‘non-local’
Bell’s theorem is often said to prove that nature isn’t “local”, that an object isn’t just directly influenced by its immediate surroundings. Another common interpretation is that it implies properties of quantum objects aren’t “real”, that they do not exist prior to measurement.
But Bell’s theorem only allows us to say that quantum physics means nature isn’t both real and local if we assume a few other things at the same time. These assumptions include the idea that measurements only have a single outcome (and not multiple, perhaps in parallel worlds), that cause and effect flow forward in time and that we do not live in a “clockwork universe” in which everything has been predetermined since the dawn of time.

Despite Bell’s theorem, nature may well be real and local, if you allowed for breaking some other things we consider common sense, such as time moving forward. And further research will hopefully narrow down the great number of potential interpretations of quantum mechanics. However, most options on the table — for example, time flowing backwards, or the absence of free will — are at least as absurd as giving up on the concept of local reality.
4. Nobody understands quantum mechanics
A classic quote (attributed to physicist Richard Feynman, but in this form also paraphrasing Niels Bohr) surmises: “If you think you understand quantum mechanics, you don’t understand it.”
This view is widely held in public. Quantum physics is supposedly impossible to understand, including by physicists. But from a 21st-century perspective, quantum physics is neither mathematically nor conceptually particularly difficult for scientists. We understand it extremely well, to a point where we can predict quantum phenomena with high precision, simulate highly complex quantum systems and even start to build quantum computers.
Superposition and entanglement, when explained in the language of quantum information, requires no more than high-school mathematics. Bell’s theorem doesn’t require any quantum physics at all. It can be derived in a few lines using probability theory and linear algebra.
Where the true difficulty lies, perhaps, is in how to reconcile quantum physics with our intuitive reality. Not having all the answers won’t stop us from making further progress with quantum technology. We can simply just shut up and calculate.
Fortunately for humanity, Nobel winners Aspect, Clauser, and Zeilinger refused to shut up and kept asking why. Others like them may one day help reconcile quantum weirdness with our experience of reality.
Alessandro Fedrizzi, Professor of Physics, Heriot-Watt University and Mehul Malik, Professor of Physics, Heriot-Watt University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.

















